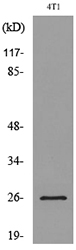
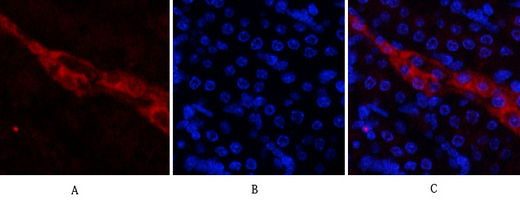
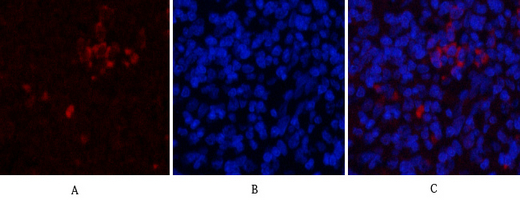
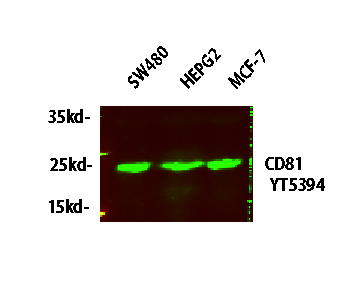
产品名称
CD81 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
别名
CD81; TAPA1; TSPAN28; CD81 antigen; 26 kDa cell surface protein TAPA-1; Target of the antiproliferative antibody 1; Tetraspanin-28; Tspan-28; CD81
存储缓冲液
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% New type preservative N.
Human Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=975
Human Swissprot No.
P60033
Human Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P60033/entry
Mouse Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=12520
Mouse Swissprot No.
P35762
Mouse Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35762
Rat Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=25621
Rat Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q62745
免疫原
The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD81. AA range:111-160
特异性
CD81 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of CD81 protein.
宿主
Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
背景介绍
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. This encoded protein is a cell surface glycoprotein that is known to complex with integrins. This protein appears to promote muscle cell fusion and support myotube maintenance. Also it may be involved in signal transduction. This gene is localized in the tumor-suppressor gene region and thus it is a candidate gene for malignancies. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014],
组织表达
Expressed on B cells (at protein level) (PubMed:20237408). Expressed in hepatocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:12483205). Expressed in monocytes/macrophages (at protein level) (PubMed:12796480). Expressed on both naive and memory CD4-positive T cells (at protein level) (PubMed:22307619).
细胞定位
Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Basolateral cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Associates with CLDN1 and the CLDN1-CD81 complex localizes to the basolateral cell membrane. .
功能
function:May play an important role in the regulation of lymphoma cell growth. Interacts with a 16-kDa Leu-13 protein to form a complex possibly involved in signal transduction. May acts a the viral receptor for HCV.,PTM:Not glycosylated.,similarity:Belongs to the tetraspanin (TM4SF) family.,subunit:Plays a critical role in HCV attachment and/or cell entry by interacting with HCV E1/E2 glycoproteins heterodimer. Interacts directly with IGSF8.,tissue specificity:Hematolymphoid, neuroectodermal and mesenchymal tumor cell lines.,
纯化
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.