PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
产品基本信息
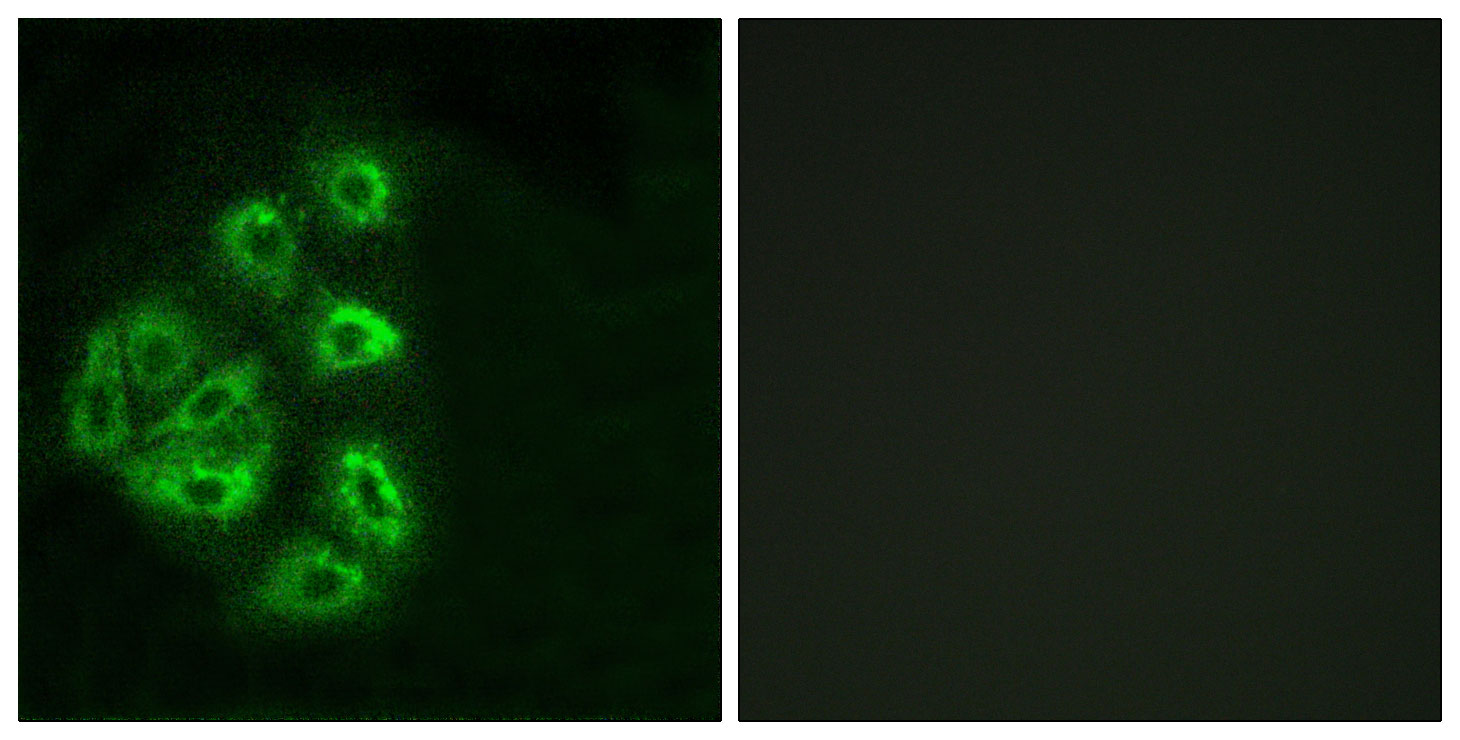
Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells, using PI3-kinase p85-alpha/gamma Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
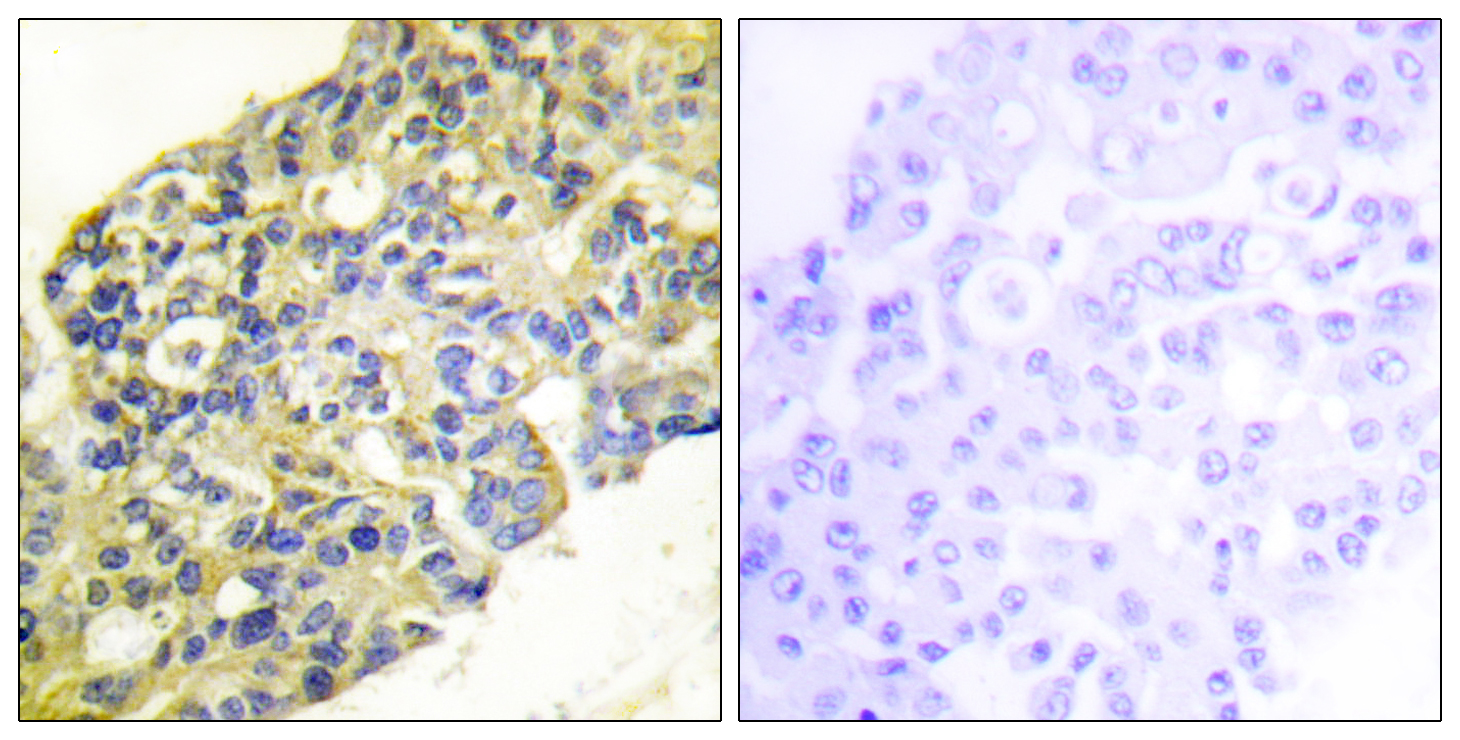
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue, using PI3-kinase p85-alpha/gamma Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
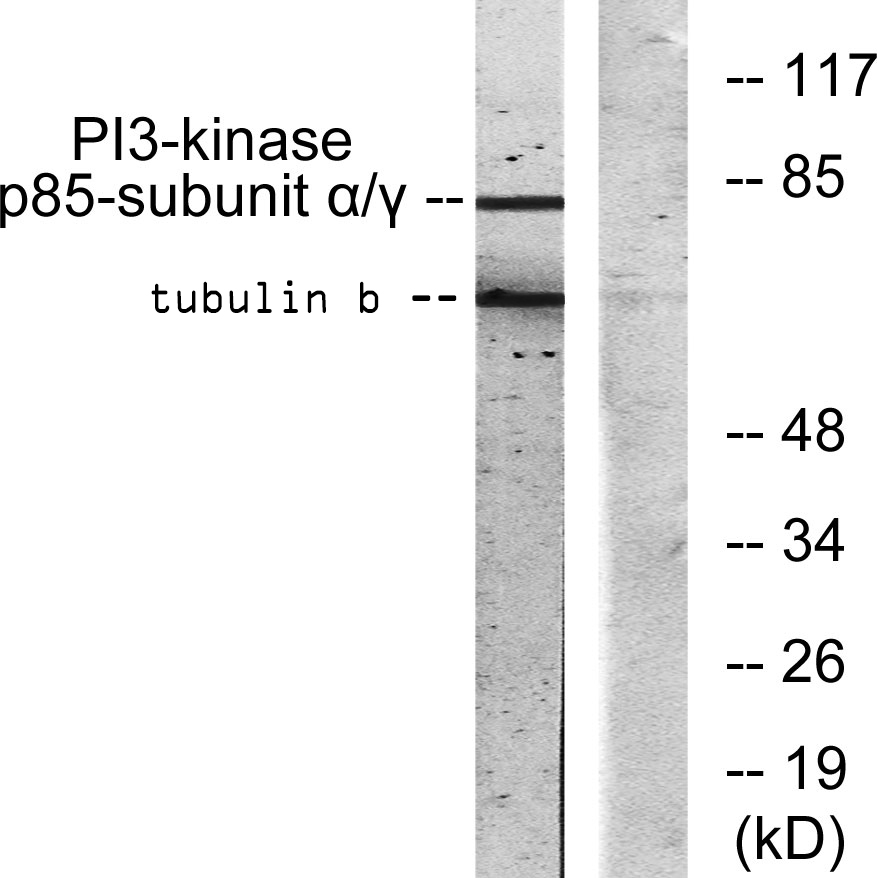
Western blot analysis of lysates from COS7 cells, treated with H2O2 100uM 30‘, using PI3-kinase p85-alpha/gamma Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
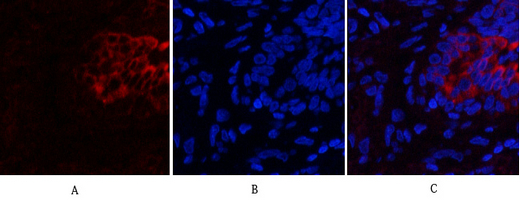
Immunofluorescence analysis of human-lung tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody(red) was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Cy3 labled Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:300(room temperature, 50min).3, Picture B: DAPI(blue) 10min. Picture A:Target. Picture B: DAPI. Picture C: merge of A+B
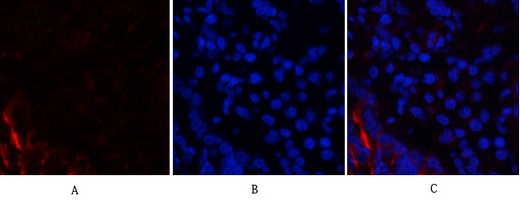
Immunofluorescence analysis of rat-lung tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody(red) was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Cy3 labled Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:300(room temperature, 50min).3, Picture B: DAPI(blue) 10min. Picture A:Target. Picture B: DAPI. Picture C: merge of A+B
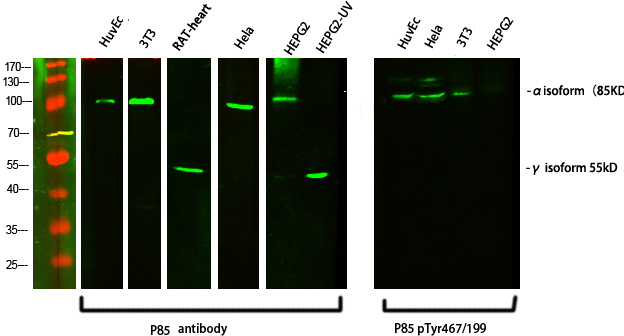
Western Blot analysis of various cells using primary antibody diluted at 1:1000(4°C overnight). Secondary antibody:Goat Anti-rabbit IgG IRDye 800( diluted at 1:5000, 25°C, 1 hour)
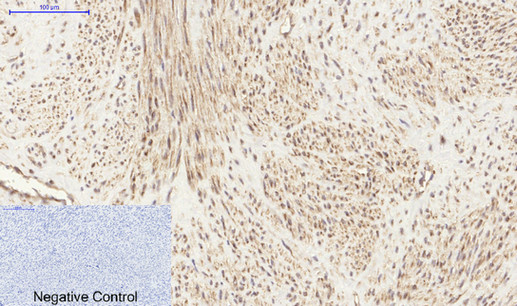
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-uterus tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antibody retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room tempeRature, 30min). Negative control was used by secondary antibody only.
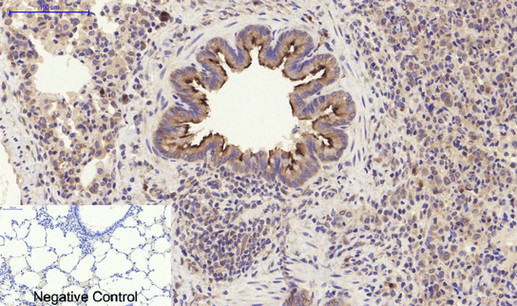
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Rat-lung tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antibody retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room tempeRature, 30min). Negative control was used by secondary antibody only.
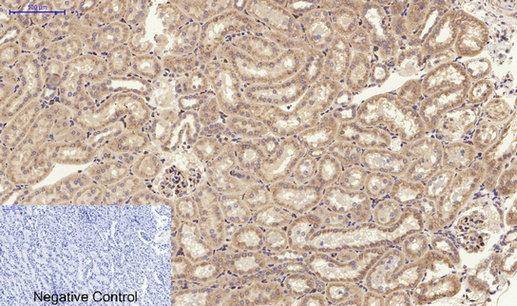
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Rat-kidney tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antibody retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room tempeRature, 30min). Negative control was used by secondary antibody only.
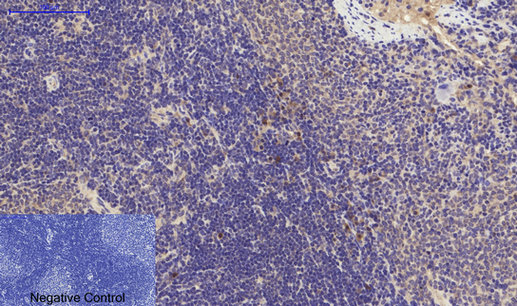
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Rat-spleen tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antibody retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room tempeRature, 30min). Negative control was used by secondary antibody only.
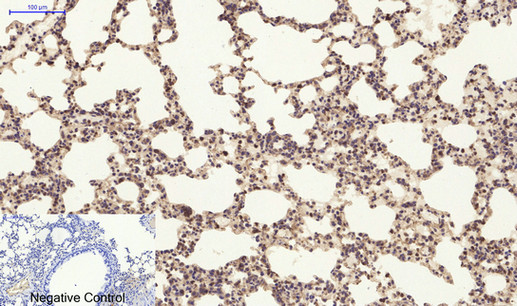
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Mouse-lung tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antibody retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room tempeRature, 30min). Negative control was used by secondary antibody only.
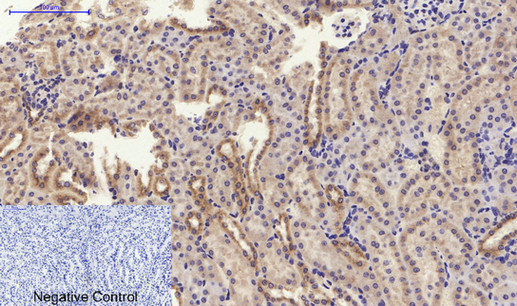
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Mouse-kidney tissue. 1,PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4°C,overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antibody retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room tempeRature, 30min). Negative control was used by secondary antibody only.
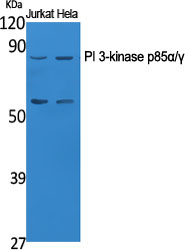
Western Blot analysis of various cells using PI 3-kinase p85α/γ Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
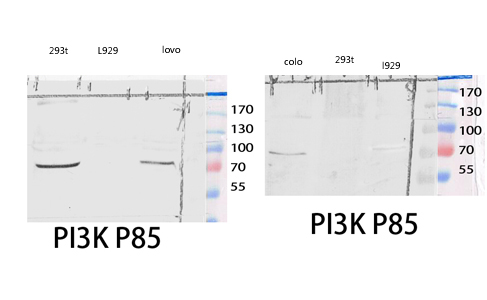
Western blot analysis of 293T COLO lysis using PI 3-kinase p85α/γ antibody.
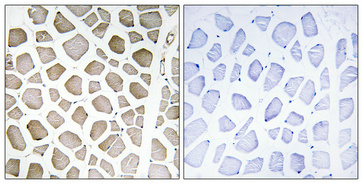
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human skeletal muscle. Antibody was diluted at 1:100(4°,overnight). High-pressure and temperature Tris-EDTA,pH8.0 was used for antigen retrieval. Negetive contrl (right) obtaned from antibody was pre-absorbed by immunogen peptide.
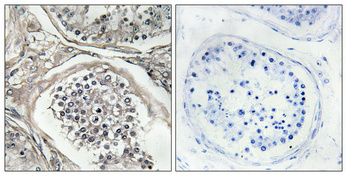
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human testis. Antibody was diluted at 1:100(4°,overnight). High-pressure and temperature Tris-EDTA,pH8.0 was used for antigen retrieval. Negetive contrl (right) obtaned from antibody was pre-absorbed by immunogen peptide.
相关文献
产品问答
相关产品

市场:027-65023363 行政/人事:027-62439686 邮箱:marketing@brainvta.com 客服:18140661572(活动咨询、售后反馈等)
销售总监:张经理 18995532642 华东区:陈经理 18013970337 华南区:王经理 13100653525 华中/西区:杨经理 18186518905 华北区:张经理 18893721749
地址:中国武汉东湖高新区光谷七路128号中科开物产业园1号楼
Copyright © 武汉枢密脑科学技术有限公司. All RIGHTS RESERVED.
鄂ICP备2021009124号 DIGITAL BY VTHINK