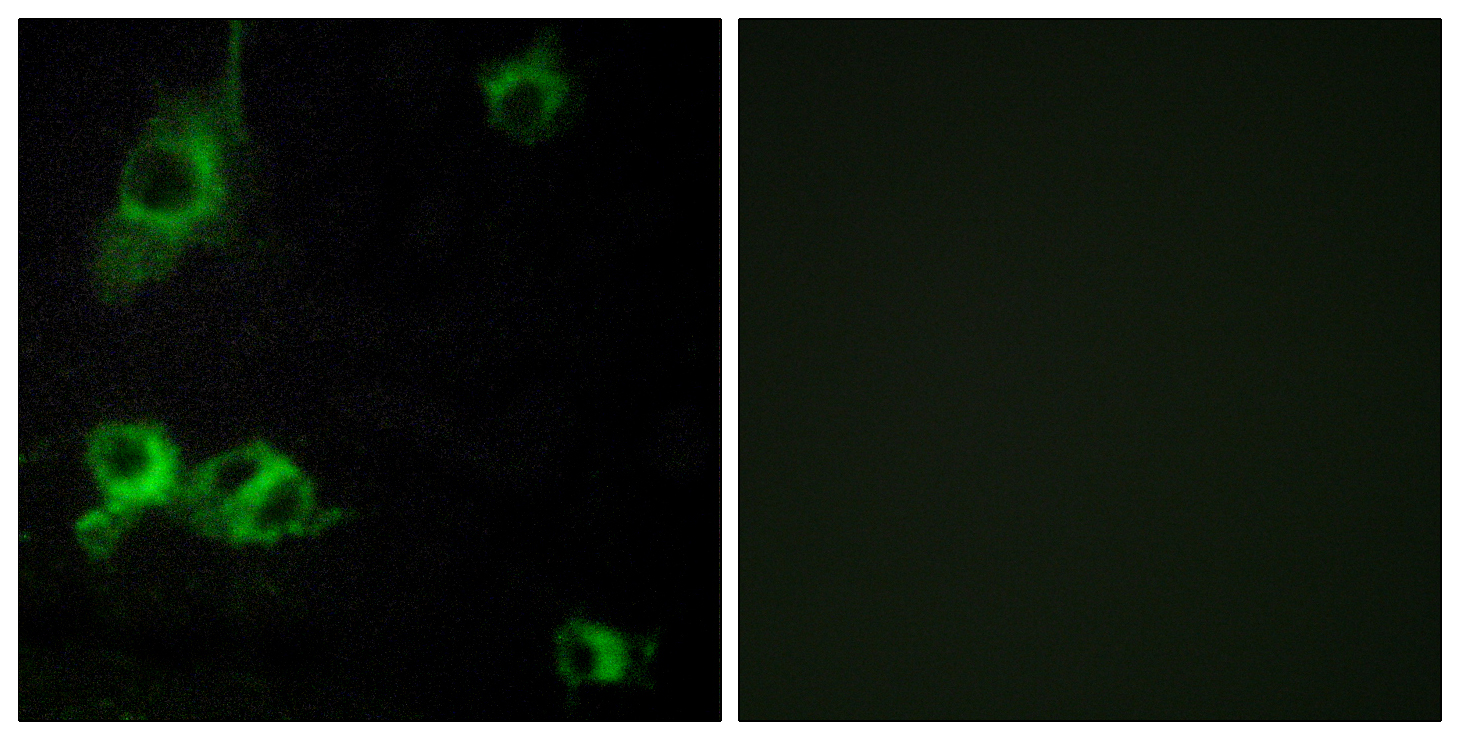
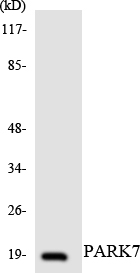产品名称
Laminin α-1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
别名
LAMA1; LAMA; Laminin subunit alpha-1; Laminin A chain; Laminin-1 subunit alpha; Laminin-3 subunit alpha; S-laminin subunit alpha; S-LAM alpha
蛋白名称
Laminin subunit alpha-1
存储缓冲液
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% New type preservative N.
Human Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=284217
Human Swissprot No.
P25391
Human Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P25391/entry
Mouse Swissprot No.
P19137
Mouse Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19137
免疫原
The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human LAMA1. AA range:2501-2550
特异性
Laminin α-1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Laminin α-1 protein.
宿主
Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
背景介绍
This gene encodes one of the alpha 1 subunits of laminin. The laminins are a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins that have a heterotrimeric structure consisting of an alpha, beta and gamma chain. These proteins make up a major component of the basement membrane and have been implicated in a wide variety of biological processes including cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, signaling, neurite outgrowth and metastasis. Mutations in this gene may be associated with Poretti-Boltshauser syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014],
组织表达
Liver,Placenta,Skin,
细胞定位
Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix, basement membrane. Major component.
信号通路
Focal adhesion;ECM-receptor interaction;Pathways in cancer;Small cell lung cancer;
功能
domain:Domains VI, IV and G are globular.,domain:The alpha-helical domains I and II are thought to interact with other laminin chains to form a coiled coil structure.,function:Binding to cells via a high affinity receptor, laminin is thought to mediate the attachment, migration and organization of cells into tissues during embryonic development by interacting with other extracellular matrix components.,similarity:Contains 1 laminin N-terminal domain.,similarity:Contains 17 laminin EGF-like domains.,similarity:Contains 2 laminin IV type A domains.,similarity:Contains 5 laminin G-like domains.,subcellular location:Major component.,subunit:Laminin is a complex glycoprotein, consisting of three different polypeptide chains (alpha, beta, gamma), which are bound to each other by disulfide bonds into a cross-shaped molecule comprising one long and three short arms with globules at each end. Alpha-1 is a subunit of laminin-1 (EHS laminin) and laminin-3 (S-laminin).,
纯化
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.