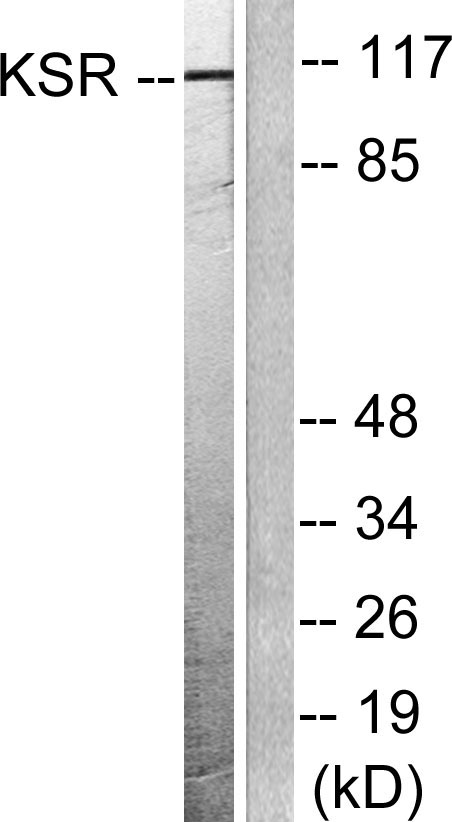
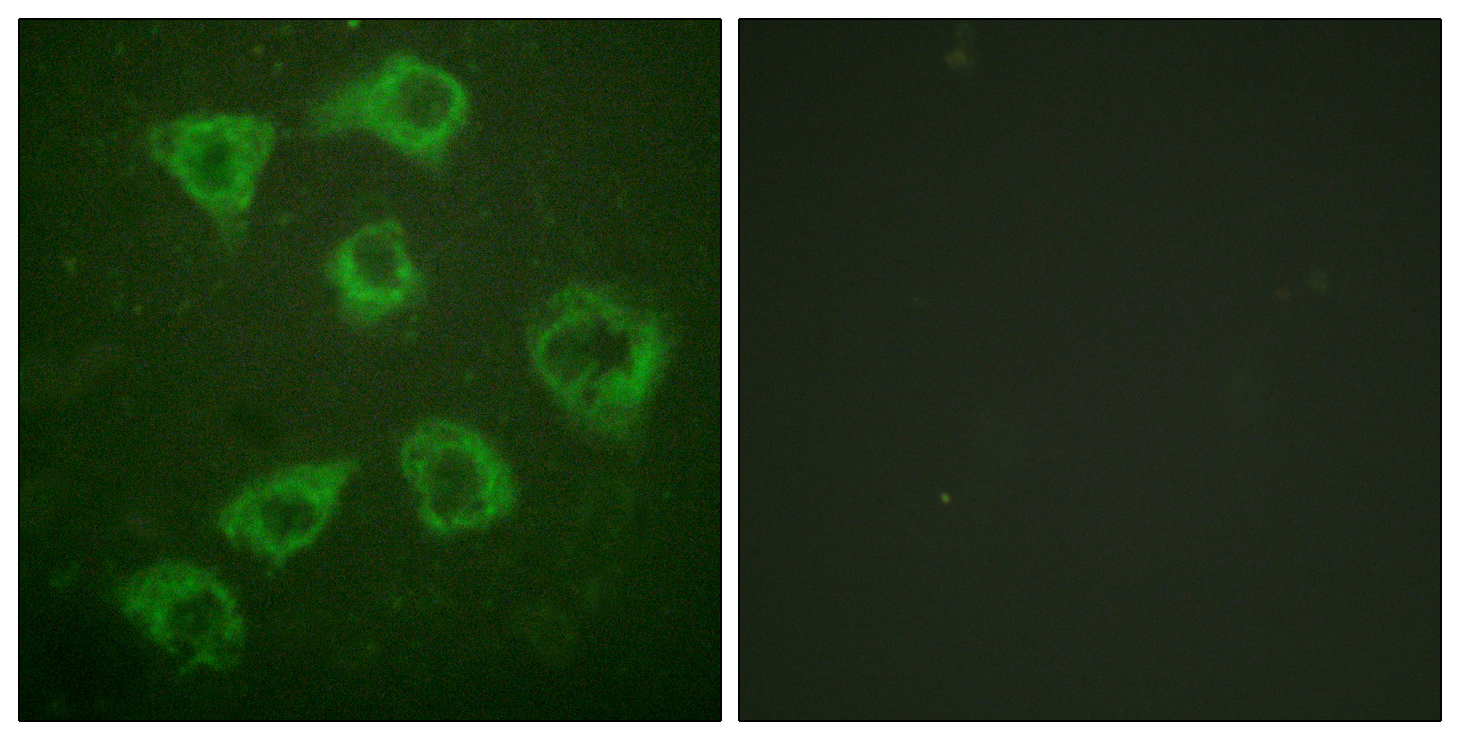
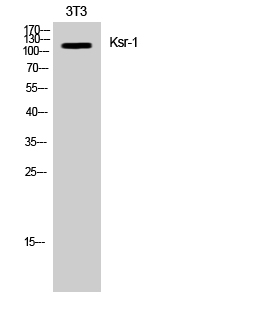
产品名称
Ksr-1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
别名
KSR1; KSR; Kinase suppressor of Ras 1
蛋白名称
Kinase suppressor of Ras 1
存储缓冲液
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% New type preservative N.
Human Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=8844
Human Swissprot No.
Q8IVT5
Human Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/Q8IVT5/entry
Mouse Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=16706
Mouse Swissprot No.
Q61097
Mouse Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q61097
免疫原
The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human KSR. AA range:358-407
特异性
Ksr-1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Ksr-1 protein.
宿主
Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
背景介绍
caution:The sequence shown here is derived from an Ensembl automatic analysis pipeline and should be considered as preliminary data.,function:Location-regulated scaffolding protein connecting MEK to RAF. Promotes MEK and RAF phosphorylation and activity through assembly of an activated signaling complex. By itself, it has no demonstrated kinase activity.,PTM:Phosphorylated on Ser-309 and, to a higher extent, on Ser-404 by MARK3. Dephosphorylated on Ser-404 by PPP2CA. In resting cells, phosphorylated KSR1 is cytoplasmic and in stimulated cells, dephosphorylated KSR1 is membrane-associated.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family.,similarity:Contains 1 phorbol-ester/DAG-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,subcellular location:In unstimulated cells, where the phosphorylated form is bound to a 14-3-3 protein, sequestration in the cytoplasm occurs. Following growth factor treatment, the protein is free for membrane translocation, and it moves from the cytoplasm to the cell periphery.,subunit:Interacts with HSPCA/HSP90, YWHAB/14-3-3, CDC37, MAP2K/MEK, MARK3, PPP2R1A and PPP2CA. Also interacts with RAF and MAPK/ERK, in a Ras-dependent manner (By similarity). The binding of 14-3-3 proteins to phosphorylated KSR prevents the membrane localization.,
组织表达
Brain,Epithelium,Platelet,Synovial membrane,
细胞定位
Cytoplasm . Membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein . Cell membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein . Cell projection, ruffle membrane . Endoplasmic reticulum membrane . In unstimulated cells, where the phosphorylated form is bound to a 14-3-3 protein, sequestration in the cytoplasm occurs. Following growth factor treatment, the protein is free for membrane translocation, and it moves from the cytoplasm to the cell periphery. .
功能
caution:The sequence shown here is derived from an Ensembl automatic analysis pipeline and should be considered as preliminary data.,function:Location-regulated scaffolding protein connecting MEK to RAF. Promotes MEK and RAF phosphorylation and activity through assembly of an activated signaling complex. By itself, it has no demonstrated kinase activity.,PTM:Phosphorylated on Ser-309 and, to a higher extent, on Ser-404 by MARK3. Dephosphorylated on Ser-404 by PPP2CA. In resting cells, phosphorylated KSR1 is cytoplasmic and in stimulated cells, dephosphorylated KSR1 is membrane-associated.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family.,similarity:Contains 1 phorbol-ester/DAG-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,subcellular location:In unstimulated cells, where the phosphorylated form is bound to a 14-3-3 protein, sequestration in the cytoplasm occurs. Following growth factor treatment, the protein is free for membrane translocation, and it moves from the cytoplasm to the cell periphery.,subunit:Interacts with HSPCA/HSP90, YWHAB/14-3-3, CDC37, MAP2K/MEK, MARK3, PPP2R1A and PPP2CA. Also interacts with RAF and MAPK/ERK, in a Ras-dependent manner (By similarity). The binding of 14-3-3 proteins to phosphorylated KSR prevents the membrane localization.,
纯化
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.