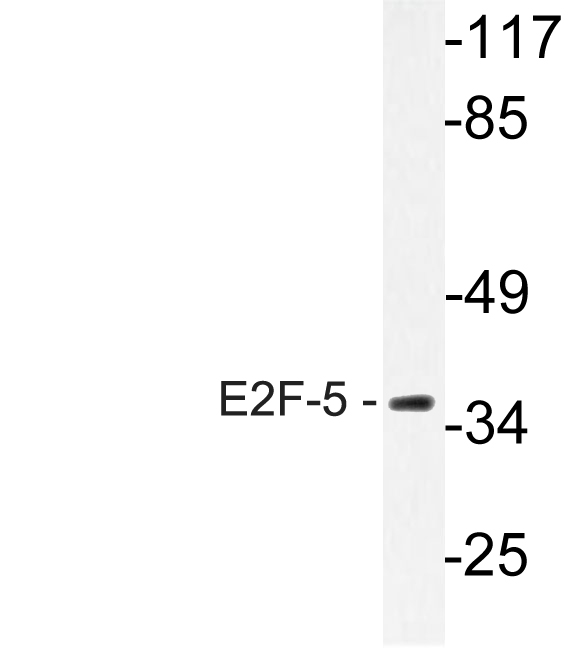
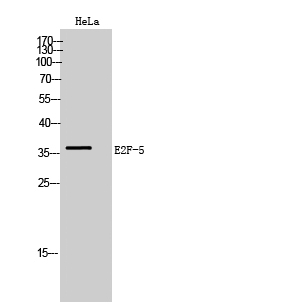
产品名称
E2F-5 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
别名
E2F5; Transcription factor E2F5; E2F-5
蛋白名称
Transcription factor E2F5
存储缓冲液
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% New type preservative N.
Human Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=1875
Human Swissprot No.
Q15329
Human Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/Q15329/entry
Mouse Gene Link
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&term=13559
Mouse Swissprot No.
Q61502
Mouse Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q61502
Rat Swissprot Link
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q62814
免疫原
The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human E2F-5. AA range:93-142
特异性
E2F-5 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of E2F-5 protein.
宿主
Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
背景介绍
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the E2F family of transcription factors. The E2F family plays a crucial role in the control of cell cycle and action of tumor suppressor proteins and is also a target of the transforming proteins of small DNA tumor viruses. The E2F proteins contain several evolutionarily conserved domains that are present in most members of the family. These domains include a DNA binding domain, a dimerization domain which determines interaction with the differentiation regulated transcription factor proteins (DP), a transactivation domain enriched in acidic amino acids, and a tumor suppressor protein association domain which is embedded within the transactivation domain. This protein is differentially phosphorylated and is expressed in a wide variety of human tissues. It has higher identity to E2F4 than to other family members. Both this protein and E2F4 inter
组织表达
Brain,Colon carcinoma,Fetal lung,Placenta,
信号通路
Cell_Cycle_G1S;Cell_Cycle_G2M_DNA;TGF-beta;
功能
function:Transcriptional activator that binds to E2F sites, these sites are present in the promoter of many genes whose products are involved in cell proliferation. May mediate growth factor-initiated signal transduction. It is likely involved in the early responses of resting cells to growth factor stimulation.,similarity:Belongs to the E2F/DP family.,subunit:Component of the DRTF1/E2F transcription factor complex. Binds cooperatively with DP-1 to E2F sites. Interaction with retinoblastoma protein RB1 or proteins RBL1 and RBL2 inhibits the E2F transactivation domain. Component of the DREAM complex (also named LINC complex) at least composed of E2F4, E2F5, LIN9, LIN37, LIN52, LIN54, MYBL1, MYBL2, RBL1, RBL2, RBBP4, TFDP1 and TFDP2. The complex exists in quiescent cells where it represses cell cycle-dependent genes. It dissociates in S phase when LIN9, LIN37, LIN52 and LIN54 form a subcomplex that binds to MYBL2.,
纯化
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.