CBL (9Y9) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
产品基本信息
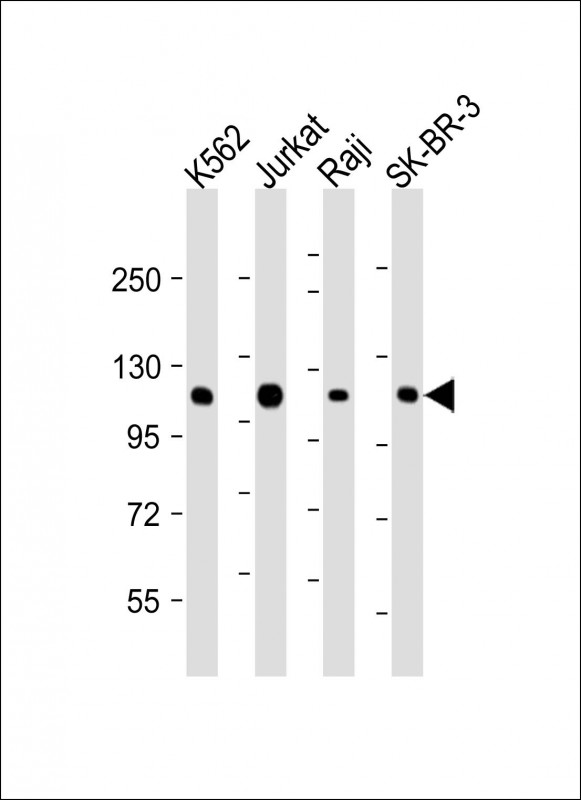
All lanes : Anti-CBL Antibody at 1:2000 dilution Lane 1: K562 whole cell lysate Lane 2: Jurkat whole cell lysate Lane 3: Raji whole cell lysate Lane 4: SK-BR-3 whole cell lysate Lysates/proteins at 20 μg per lane. Secondary Goat Anti-mouse IgG, (H+L), Peroxidase conjugated at 1/10000 dilution. Predicted band size : 100 kDa Blocking/Dilution buffer: 5% NFDM/TBST.
相关文献
产品问答
相关产品

市场:027-65023363 行政/人事:027-62439686 邮箱:marketing@brainvta.com 客服:18140661572(活动咨询、售后反馈等)
销售总监:张经理 18995532642 华东区:陈经理 18013970337 华南区:王经理 13100653525 华中/西区:杨经理 18186518905 华北区:张经理 18893721749
地址:中国武汉东湖高新区光谷七路128号中科开物产业园1号楼
Copyright © 武汉枢密脑科学技术有限公司. All RIGHTS RESERVED.
鄂ICP备2021009124号 DIGITAL BY VTHINK