产品名称
LAMP2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
别名
Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2, LAMP-2, Lysosome-associated membrane protein 2, CD107 antigen-like family member B, CD107b, LAMP2
存储缓冲液
Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) New?type?preservative?N. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification.
Human Gene ID
NP_001116078.1;NP_002285.1;NP_054701.1
Human Swissprot No.
P13473
特异性
This LAMP2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with LAMP2 recombinant protein.
运输及保存条件
Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles.
背景介绍
LAMP2 is a member of a family of membrane glycoproteins. This glycoprotein provides selectins with carbohydrate ligands. It may play a role in tumor cell metastasis. It may also function in the protection, maintenance, and adhesion of the lysosome.
组织表达
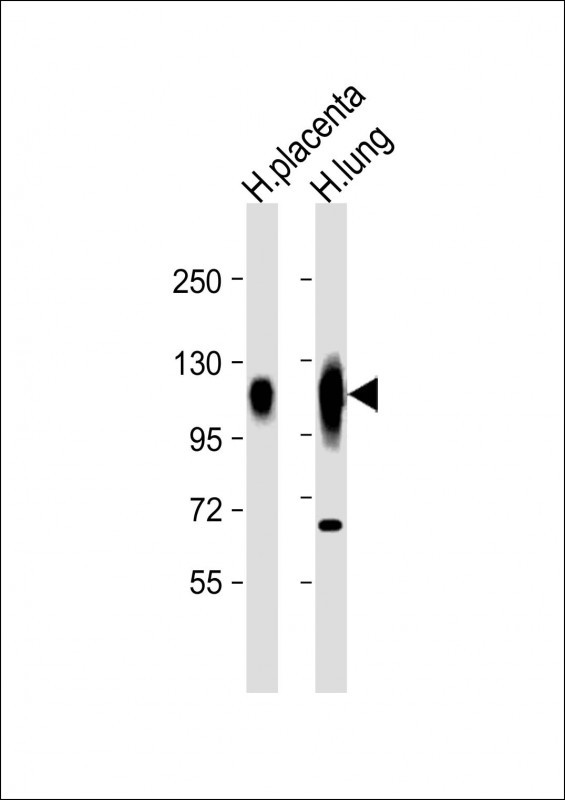
Isoform LAMP-2A is highly expressed in placenta, lung and liver, less in kidney and pancreas, low in brain and skeletal muscle (PubMed:7488019, PubMed:26856698). Isoform LAMP-2B is detected in spleen, thymus, prostate, testis, small intestine, colon, skeletal muscle, brain, placenta, lung, kidney, ovary and pancreas and liver (PubMed:7488019, PubMed:26856698). Isoform LAMP-2C is detected in small intestine, colon, heart, brain, skeletal muscle, and at lower levels in kidney and placenta (PubMed:26856698).
细胞定位
Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17897319} Endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17897319}. Lysosome membrane {ECO:0000255|PROSITE- ProRule:PRU00740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11082038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17897319, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18644871, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2912382}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17897319} Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17047}. Note=This protein shuttles between lysosomes, endosomes, and the plasma membrane
功能
Plays an important role in chaperone-mediated autophagy, a process that mediates lysosomal degradation of proteins in response to various stresses and as part of the normal turnover of proteins with a long biological half-live (PubMed:
8662539, PubMed:
11082038, PubMed:
18644871, PubMed:
24880125, PubMed:
27628032). Functions by binding target proteins, such as GAPDH and MLLT11, and targeting them for lysosomal degradation (PubMed:
8662539, PubMed:
11082038, PubMed:
18644871, PubMed:
24880125). Plays a role in lysosomal protein degradation in response to starvation (By similarity). Required for the fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes during autophagy (PubMed:
27628032). Cells that lack LAMP2 express normal levels of VAMP8, but fail to accumulate STX17 on autophagosomes, which is the most likely explanation for the lack of fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes (PubMed:
27628032). Required for normal degradation of the contents of autophagosomes (PubMed:
27628032). Required for efficient MHCII-mediated presentation of exogenous antigens via its function in lysosomal protein degradation; antigenic peptides generated by proteases in the endosomal/lysosomal compartment are captured by nascent MHCII subunits (PubMed:
20518820). Is not required for efficient MHCII-mediated presentation of endogenous antigens (PubMed:
20518820).