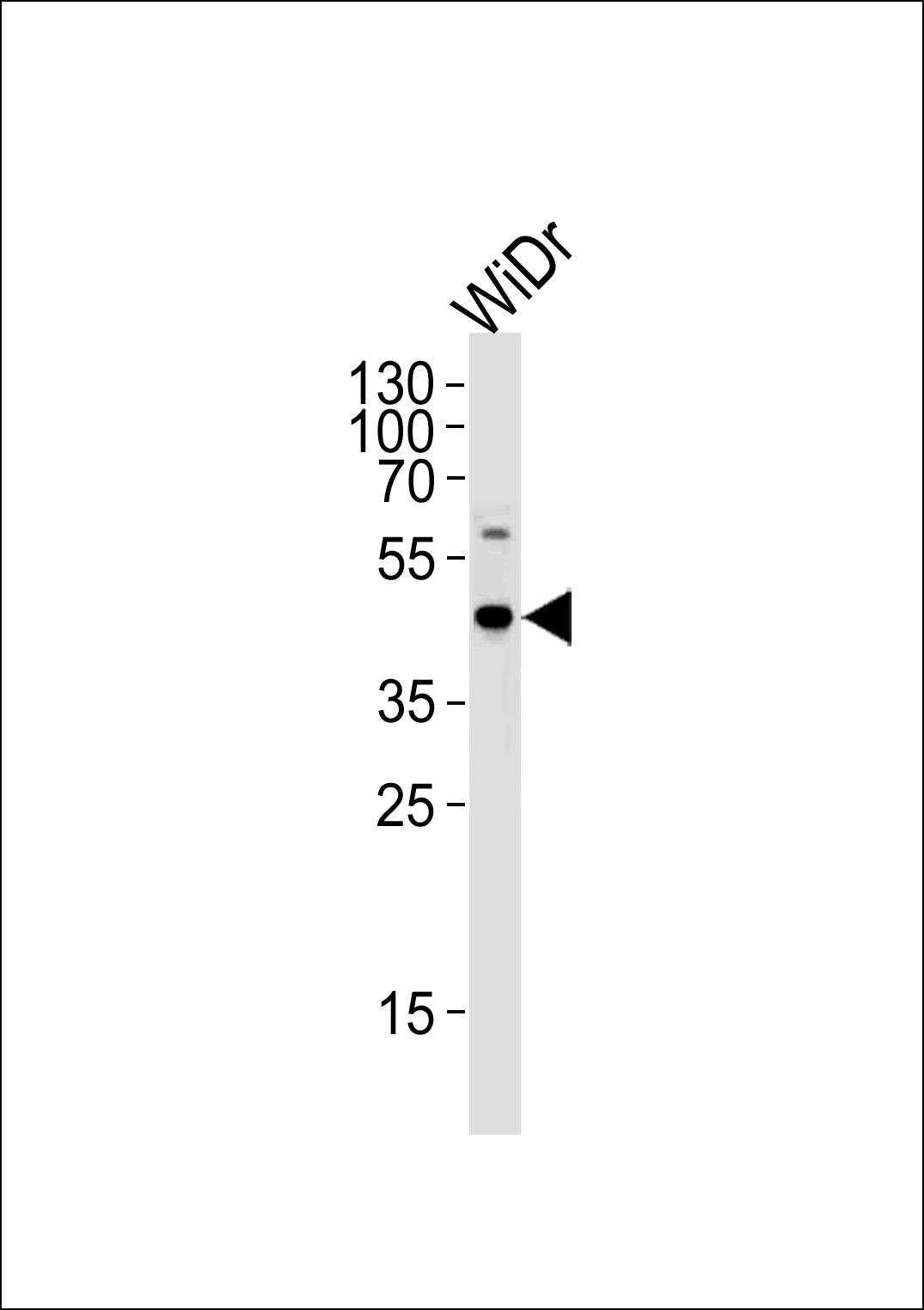
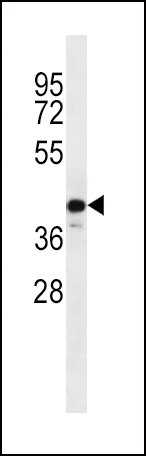
Component of the C9orf72-SMCR8 complex, a complex that has guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity and regulates autophagy (PubMed:
27193190, PubMed:
27103069, PubMed:
27617292, PubMed:
28195531). In the complex, C9orf72 and SMCR8 probably constitute the catalytic subunits that promote the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound RAB8A and RAB39B into their active GTP- bound form, thereby promoting autophagosome maturation (PubMed:
27103069). The C9orf72-SMCR8 complex also acts as a regulator of autophagy initiation by interacting with the ATG1/ULK1 kinase complex and modulating its protein kinase activity (PubMed:
27617292). Positively regulates initiation of autophagy by regulating the RAB1A- dependent trafficking of the ATG1/ULK1 kinase complex to the phagophore which leads to autophagosome formation (PubMed:
27334615). Acts as a regulator of mTORC1 signaling by promoting phosphorylation of mTORC1 substrates (PubMed:
27559131). Plays a role in endosomal trafficking (PubMed:
24549040). May be involved in regulating the maturation of phagosomes to lysosomes (By similarity). Regulates actin dynamics in motor neurons by inhibiting the GTP-binding activity of ARF6, leading to ARF6 inactivation (PubMed:
27723745). This reduces the activity of the LIMK1 and LIMK2 kinases which are responsible for phosphorylation and inactivation of cofilin, leading to cofilin activation (PubMed:
27723745). Positively regulates axon extension and axon growth cone size in spinal motor neurons (PubMed:
27723745). Plays a role within the hematopoietic system in restricting inflammation and the development of autoimmunity (By similarity).