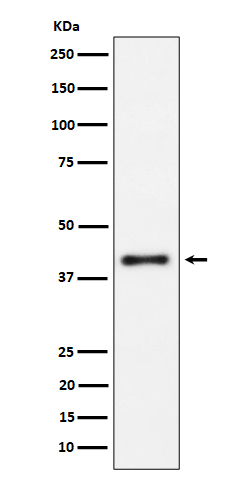
产品名称
IL15RA (16Y9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
别名
CD215; IL 15R alpha; IL-15 receptor subunit alpha; IL-15R-alpha; IL-15RA; Il15ra; Interleukin 15 receptor alpha; sIL-15 receptor subunit alpha; sIL-15R-alpha; sIL-15RA ; Soluble interleukin 15 receptor subunit alpha;
纯度
Affinity-chromatography
存储缓冲液
Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% New type preservative N and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
Human Swissprot No.
Q13261
注意事项
IL15RA Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
组织表达
Expressed in neutrophils (at protein level) (PubMed:15123770). Expressed in fetal brain with higher expression in the hippocampus and cerebellum than in cortex and thalamus (PubMed:12114302). Higher levels of soluble sIL-15RA form in comparison with membrane-bound forms is present in all brain structures (PubMed:12114302). Isoforms 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9: Widely expressed (PubMed:10480910, PubMed:8530383).
细胞定位
Membrane; Single- pass type I membrane protein. Nucleus membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell surface. Note=Mainly found associated with the nuclear membrane [Isoform 6]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane; Single- pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein Note=Isoform 5, isoform 6, isoform 7 and isoform 8 are associated with endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi and cytoplasmic vesicles, but not with the nuclear membrane [Isoform 8]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane; Single- pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein Note=Isoform 5, isoform 6, isoform 7 and isoform 8 are associated with endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi and cytoplasmic vesicles, but not with the nuclear membrane
功能
High-affinity receptor for interleukin-15 (PubMed:
8530383). Can signal both in cis and trans where IL15R from one subset of cells presents IL15 to neighboring IL2RG-expressing cells (By similarity). In neutrophils, binds and activates kinase SYK in response to IL15 stimulation (PubMed:
15123770). In neutrophils, required for IL15- induced phagocytosis in a SYK-dependent manner (PubMed:
15123770). Expression of different isoforms may alter or interfere with signal transduction (PubMed:
10480910).