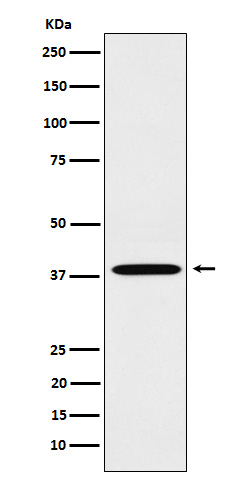
产品名称
LTB4R (3K9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
别名
BLT; BLT1; BLTR; CMKRL1; GPR16; LTB4R1; LTBR1; P2RY7; P2Y7;
纯度
Affinity-chromatography
蛋白名称
BLT, BLT1, BLTR, CMKRL1, GPR16, P2RY7
存储缓冲液
Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% New type preservative N and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
Human Swissprot No.
Q15722
注意事项
LTB4R Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
组织表达
Expressed at highest levels in heart, skeletal muscle and at lower levels in brain and liver. High level of expression in lymphoid tissues
细胞定位
Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
功能
Receptor for extracellular ATP > UTP and ADP. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. May be the cardiac P2Y receptor involved in the regulation of cardiac muscle contraction through modulation of L-type calcium currents. Is a receptor for leukotriene B4, a potent chemoattractant involved in inflammation and immune response.