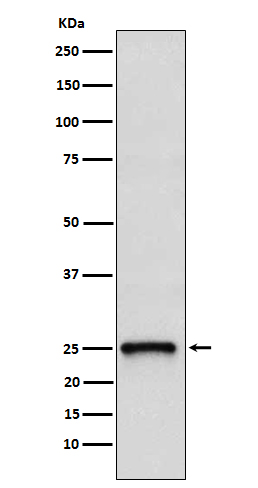
产品名称
TC10 (19O11) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
别名
ARHQ; RASL7A; Rho related GTP binding protein RhoQ; Rhoq; TC10A;
纯度
Affinity-chromatography
存储缓冲液
Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% New type preservative N and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
Human Swissprot No.
P17081
注意事项
TC10 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
细胞定位
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor
功能
Plasma membrane-associated small GTPase which cycles between an active GTP-bound and an inactive GDP-bound state. In active state binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular responses. Involved in epithelial cell polarization processes. May play a role in CFTR trafficking to the plasma membrane. Causes the formation of thin, actin-rich surface projections called filopodia.